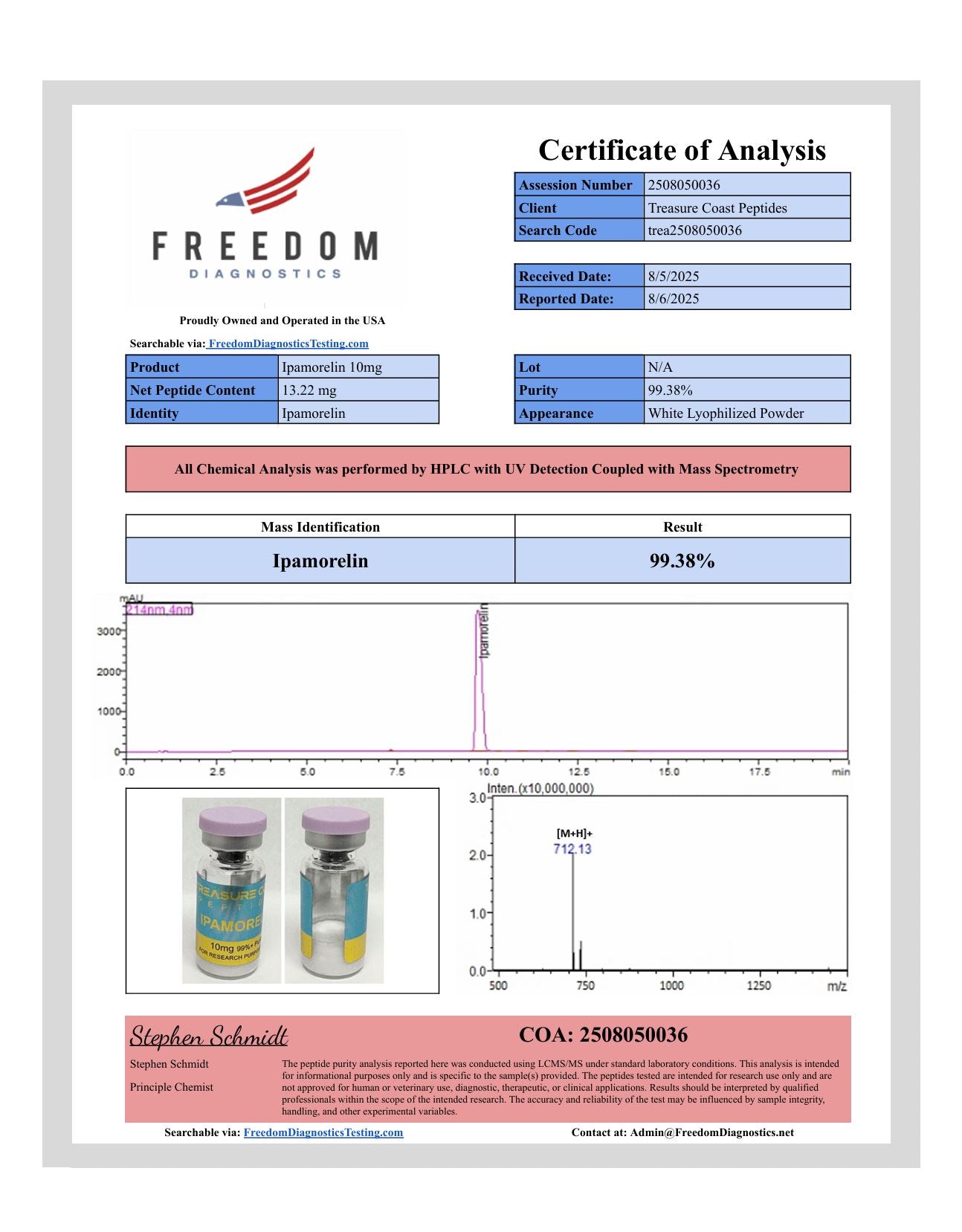
Why Choose Us?
Third-Party Tested
Third-party tested for identity, purity, & concentration
Free Shipping
Free shipping in the US for orders $150+
Satisfaction Guarantee
We guarantee you will be satisfied or your money back
Subscribe For Updates
Subscribe to our email and for our latest updates, product releases and offers.